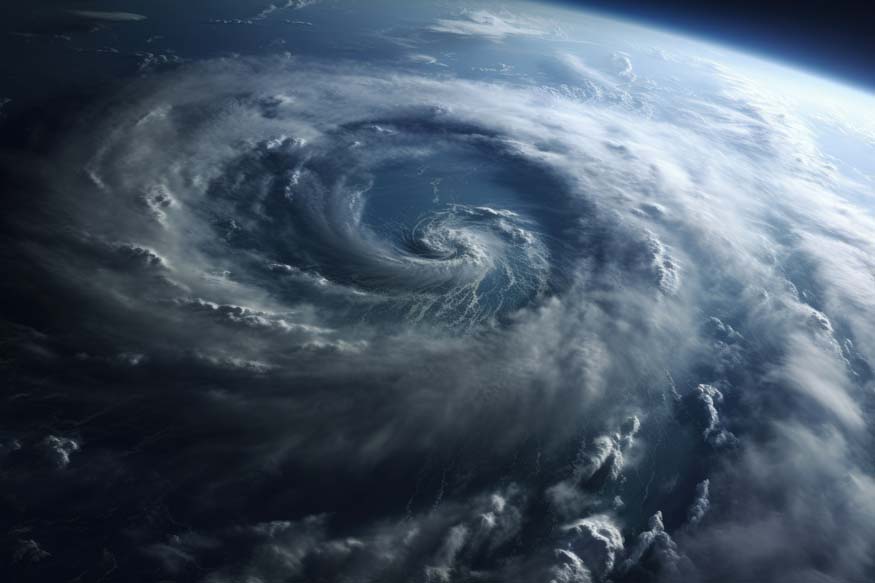
What are Cyclones?
A cyclone is a wind system that revolves inward around a powerful centre of low pressure, clockwise in the southern hemisphere and anticlockwise in the northern.
A cyclone is defined as winds exceeding 118 kmph. Cyclones are the name given to these revolving winds that originate across the Indian Ocean and south of the Pacific Ocean. In other areas, they are typically referred to by different names, including hurricanes and typhoons.
One needs to study the cyclones’ creation process and classifications to comprehend their intensity.
How Are Cyclones Formed?
The formation of a cyclone:
- Humid air over the water rises higher, leaving less air close to the ocean surface because it is less dense and warmer. This leads to the formation of a low-pressure zone.
- When air enters this low-pressure area from the nearby high-pressure areas and gradually warms up, it forms a cycle.
- The entire cloud and wind system begins to spin and expand due to the warm air’s continuous heating, rising, and evaporation process.
- The cyclone’s eye develops in the centre as it gains speed. The air with high pressure from above then flows into this tranquil, clear core zone, representing the area with the lowest air pressure. Additionally, this area receives a flow of high-pressure air from above.

What Are the Causes of a Cyclone?
Now that you have learnt about how cyclones are formed, you may also want to learn more about the causes behind cyclones.
The following are the causes of cyclone formation:
- Warm sea surface temperatures.
- The region that creates a low-pressure zone is affected by the Coriolis force.
- The instability of the atmosphere.
- Higher humidity in the troposphere lowest to middle layers.
- Minimal wind shear vertically.
- Low-level disruption or attention that already exists.
Effects of Cyclone
Tornadoes, powerful winds, a significant storm surge, and torrential rain are the main consequences of a cyclone. The intensity, location, and size of a cyclone play a major role in the destruction or property damage it causes. The major after-effects of these cyclones are devastation and destruction.
Impact of Cyclones
- It has the potential to harm infrastructure, homes, and buildings.
- It has the potential to interfere with communication, power, and transportation.
- It may result in landslides and flooding.
- It has the potential to contaminate water and increase the spread of illness.
- People may be displaced as a result.
- It may affect livelihoods and cause supply chain disruptions.
- The national economy may be significantly impacted.

Preventive Measures to Combat Cyclones
Although cyclones can have catastrophic effects, some precautions can be taken to reduce the likelihood of damage and fatalities. In order to manage the effects of a cyclone, early warning systems, evacuation plans, and disaster preparedness packs are crucial. We can be ready for anything that comes our way if we are prepared.
Preventive Measures
Early warning system: This is the first step in addressing a cyclone’s effects. Weather radios, television, and the internet are some of the means through which early warning can be communicated.
Developing an evacuation strategy: Make sure that everyone knows what actions to take before the cyclone hits. This should be communicated in advance to let people know where to go and what to do. The evacuation plan should include a safe place to stay, a designated route to follow, and a list of necessary items to bring with you.
Prepare an emergency kit: The third step in cyclone prevention is to have a disaster preparedness kit. This bag should include food, water, a torch, and a first aid kit. Having this gear will help you prepare for the cyclone’s onslaught.
We can reduce the effects of cyclones and save lives by doing these things. To cope with the effects of a cyclone, early warning systems, evacuation plans, and disaster preparedness packs are crucial. We can be ready for anything that comes our way if we are prepared.
|
S. No. |
Cyclone Name |
Location of Occurrence |
|
1 |
Biparjoy |
Arabian Sea |
|
2 |
Mocha |
Bay of Bengal |
|
3 |
Hamoon |
Bay of Bengal |
|
4 |
Remal |
Indian Ocean |
|
5 |
Asani |
Bay of Bengal |
|
6 |
Yaas |
Bay of Bengal |
|
7 |
Sitrang |
Bay of Bengal |
|
8 |
Mandous |
Bay of Bengal |
|
9 |
Tauktae |
Arabian Sea |
|
10 |
Amphan |
Bay of Bengal |
Cyclones’ impact extends beyond immediate physical destruction. They have profound economic, environmental, and social consequences, affecting millions of lives worldwide. Understanding these aspects is crucial for developing effective strategies for cyclone preparedness, mitigation, and recovery.
At Center Point School, we emphasise the importance of educating young minds about natural phenomena like cyclones. Our curriculum includes interactive learning experiences that teach children about the science behind cyclones. We also teach children safety measures during such events and the importance of environmental stewardship. Through education and awareness, children can navigate and respond to the challenges posed by natural disasters.
For more such informative/interesting blogs, visit Center Point School.